SPE11A overview
This description provides a concise overview. For an exhaustive description, please refer to Nordbotten et al. (2024a).
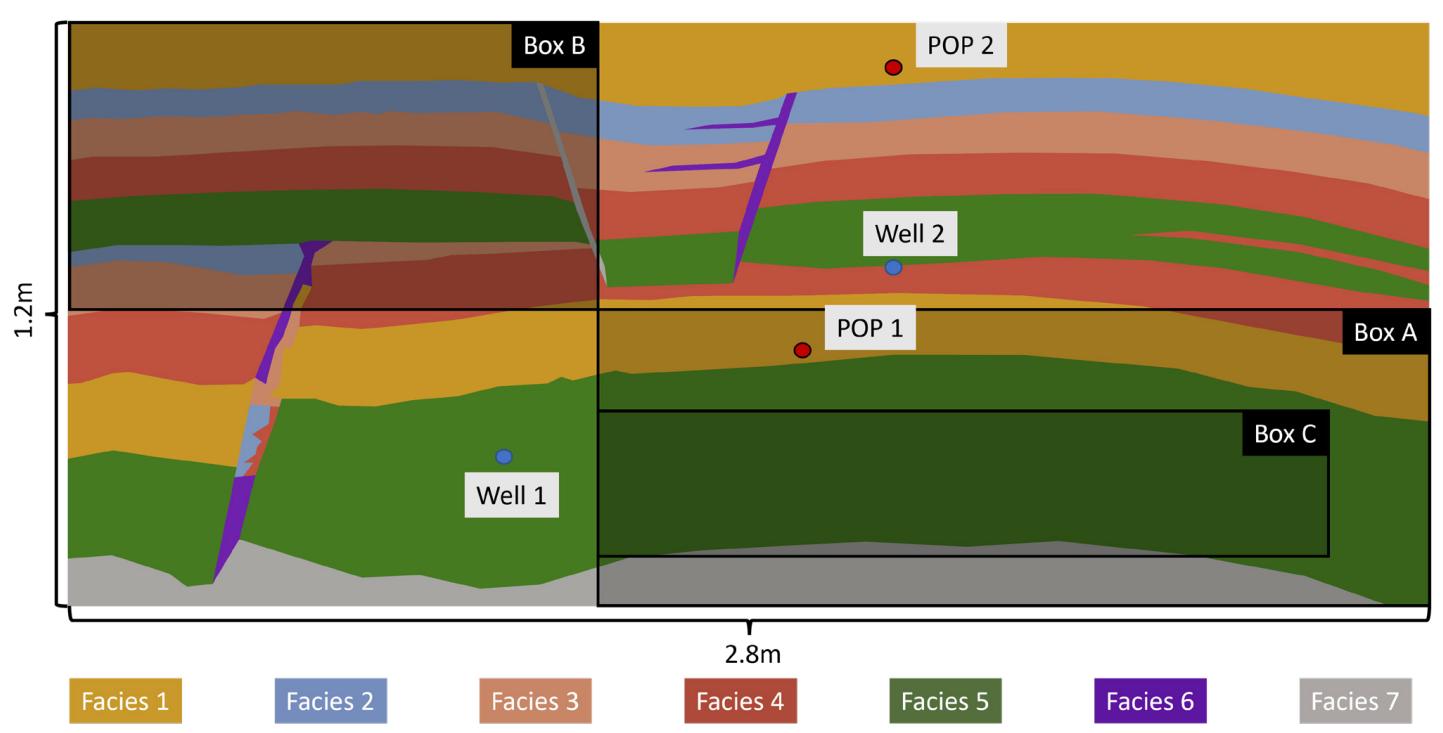
This subcase is motivated by the application of reservoir simulators to analyze laboratory-scale experiments (Fernø et al. 2024), specifically inspired by the recent FluidFlower validation study (Flemisch et al. 2024). It is characterized by the following features.
- Domain and geometry: The domain is 2.8 meters wide and 1.2 m high, and it is treated as a two-dimensional system with a nominal thickness of 1 cm used for converting to volumetric quantities.
- Boundary conditions: The top boundary is set to atmospheric pressure, while all other boundaries are defined as no-flow.
- Temperature: The system is assumed to be isothermal at 20 °C, consistent with the experimental setup.
- Facies and permeability: Facies properties are derived from unconsolidated sands, with a permeability of 4 kD in the main reservoir (facies 5) and 40 D in the seal (facies 1).
- Initial conditions: The initial condition is pure water at hydrostatic pressure.
- Injection conditions: The injection period lasts for 5 h, with a total simulation time of 120 h. The injection rate is set to 5 cm3/min for each well.
- Reporting schedule: Sparse data are reported every 10 min, while dense data are recorded hourly. The reporting grid for the dense data is a 1 cm by 1 cm Cartesian grid, that includes approximately 33,000 cells.
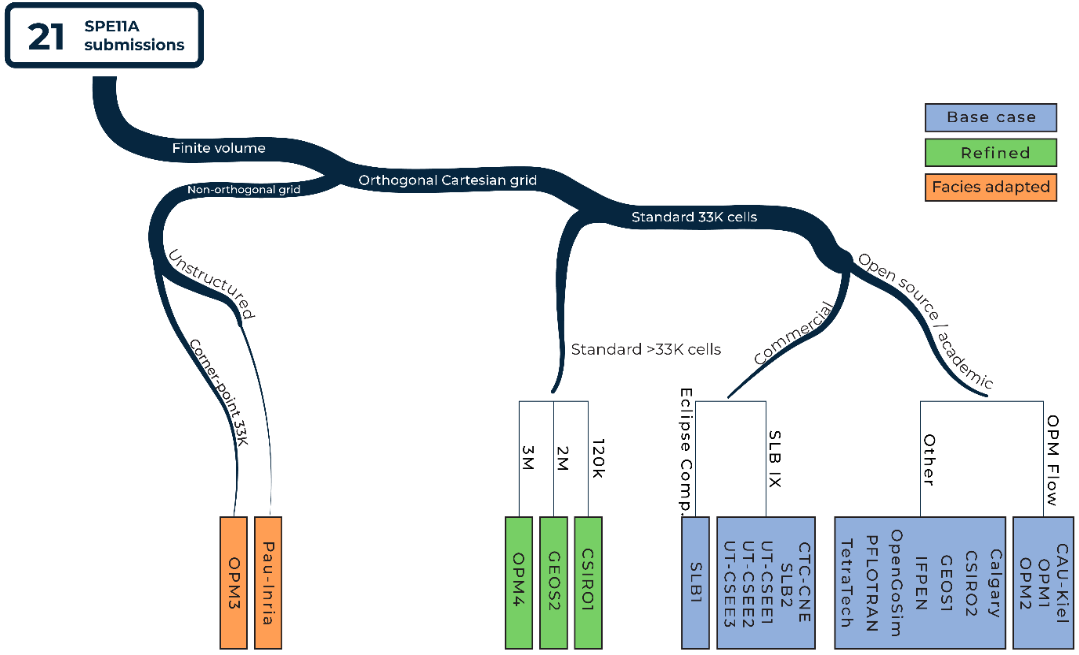
Overview over results